When you connect to the Internet, your Internet Service Provider (known as ISP) assigns an IP address. Depending on the type of service you subscribed, you may be allocated to use static or dynamic IP address. A static IP address is a permanent (non-changing) IP address assigned to you. Most users on the other hand gets an dynamically assigned IP address from their ISP. The device (a router, gateway or computer) connected to your ISP allows you to connect to the Internet, and also allows you to change its IP address. This article only pertains to changing an IP address of dynamically assigned IP address (via the DHCP).
Change your IP Country with a Virtual Private Network
You may want to change your public IP address for a variety of reasons. If your IP address is banned by certain game servers or your download allowance from a P2P network has expired, obtaining a different IP address from your current ISP will solve your problem (see instruction below). However, if you wish to bypass regional block and wish to obtain an IP address from a different country, changing an IP address from your ISP will not help you. For example, if you want to watch BBC, Netflix, Spotify or Hulu from a region where those services are blocked, you will need a VPN service to obtain an IP address of a country where the service is allowed. With VPN, you'll also surf Internet anonymously with added security.
Here are a few VPN providers we recommend:
- Hide My Ass
- Express VPN (30 Day Money Back Guarantee)
- Vypr VPN (Free Trial)
- Pure VPN (Exclusive 75% off on yearly plan to IPlocation.net visitors.)
- IP Vanish VPN
We receive compensation when a purchase is made from the referred link. Our recommendation is based on our research and positive feedback we received from the users who've used the services.
Ok, I got it so how do I change IP address?
If you renew your IP address from your current ISP, your ISP may or may not assign you a new IP address. Depending on how you're connected to the Internet, you may have to reset different device. If you're connected via a router, you'll have to change IP address of your router. If you're connected directly to the Internet via a layer-2 gateway, you'll have to change your computer's IP address. Most home network is connected via a router, so chances are that you need to change IP address of your router. In this article, I will describe how to change IP address of your router and also show you how to change IP address of your computer. There are a number of ways to change IP address, so I'll describe easiest method first and then describe a bit more complicated methods.
In order to verify that you've changed an IP address of your device, you'll have to visit Find My IP page of our website.
How to change IP address of a router?
A router is a layer 3 networking device that connects multiple computers to the Internet. In home network with dynamically assigned IP address, a router is assigned a public IP address and all the computers connected to the router is assigned a private IP address. When computers connected to the router visits the Internet, the world views your computer with a public IP address of your router. So, if you want the world to see you with a different IP address, you'll have to change IP address of your router. Here are a few ways to change IP address of your router.
- Turn off your router for a minute and turn it back on. The common nature of DHCP is to "remember" the device and assign you the same IP address you had before, so simply turning off your router and turning it back on will not likely change IP address. However, if you try multiple times you may get lucky and will obtain a new IP address from your ISP. If multiple tries doesn't get you a new IP address, try leaving the router turned off overnight and restart in the morning.
- Reconnect your router to your ISP via administrative Interface. Most routers allow you to disconnect from upstream ISP, and reconnect via a point-and-click from the Administrative Console. Each router vendor provides a different UI to achieve this, but once you login to the Administrative Console of the router you should be able to locate the reconnect button. The screenshot below is the method provided by the Asus RT-N66W model.
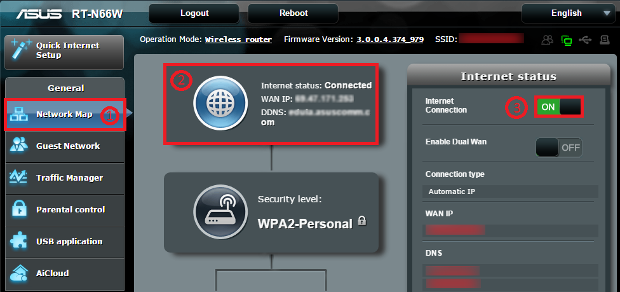
How to change IP address of a computer?
- Shutdown your computer for a minute and turn it back on. Again, the common nature of DHCP is to assign the device same IP address each time it connects to the network, it's unlikely that you'll receive different address first time your restart your computer. If you restart a few times, you may get lucky and get a new IP address from your router.
- Renew your IP address. You may manully release your IP address and obtain a new IP address with Windows ipconfig utility. Please follow the following steps.
On Windows 7 and below, click Start -> Run, and type cmd as shown below. On Windows 8, type WIN key and X key to bring Power User Menu -> Choose Run.
On the Command Prompt screen, run "ipconfig /release" and "ipconfig /renew" commands as shown below. You'll have to start Elevated Command Prompt (Run as System Administrator) to execute ipconfig command.
C:\> ipconfig
Windows IP Configuration
Ethernet adapter Wireless Network Connection:
Connection-specific DNS Suffix . :
IP Address. . . . . . . . . . . . : 192.168.1.101
Subnet Mask . . . . . . . . . . . : 255.255.255.0
Default Gateway . . . . . . . . . : 192.168.1.1
C:\> ipconfig /release
Windows IP Configuration
No operation can be performed on Local Area Connection while it has its media
disconnected.
Ethernet adapter Wireless Network Connection:
Connection-specific DNS Suffix . :
IP Address. . . . . . . . . . . . : 0.0.0.0
Subnet Mask . . . . . . . . . . . : 0.0.0.0
Default Gateway . . . . . . . . . :
Ethernet adapter Local Area Connection:
Media State . . . . . . . . . . . : Media disconnected
C:\> ipconfig /renew
Windows IP Configuration
Ethernet adapter Wireless Network Connection:
Connection-specific DNS Suffix . :
IP Address. . . . . . . . . . . . : 192.168.1.102
Subnet Mask . . . . . . . . . . . : 255.255.255.0
Default Gateway . . . . . . . . . : 192.168.1.1
Verify that you have a new IP address by either typing ipconfig command, or by visiting Find My IP page. On our example above, the IP address has been changed from 192.168.1.101 to 192.168.1.102. Again, the nature of DHCP is to assign the device same IP address as before so you may have run this step multiple times to change your IP address.
Use someone else's network
As with Hide IP Address, you can always use someone else's network and obtain an IP address from that network. Try using free Wi-Fi services from a local coffee shop, hotel, library or any other public offerings. An IP address does not travel with your computer, so using someone else's network may be a viable solution.





